It can detect a metal coin at a distance of 15 cm and a larger metal object at a distance of 40 cm and more . That's a relatively good result considering its simplicity.
Pulse Induction (PI) Metal detector use a single coil as both transmitter and receiver. This technology sends powerful, short bursts (pulses) of current through a coil of wire. Each pulse generates a brief magnetic field. When the pulse ends, the magnetic field reverses polarity and collapses very suddenly, resulting in a sharp electrical spike. This spike lasts a few microseconds and causes another current to run through the coil. This current is called the reflected pulse and is extremely short, lasting only about 30 microseconds. Another pulse is then sent and the process repeats. If a piece of metal comes inside the range of the magnetic field lines, the receive coil can detect a change in both amplitude and phase of the received signal. The amount of amplitude change and phase change is an indication for the size and distance of the metal, and can also be used to discriminate between ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
The device is very simple and easy to make and contains several components:
- Arduino Nano microcontroller
- Power Mosfet transistor
- Operational Amplifier
- Few resistors and capacitors
- Search coil
- And Leds and Buzzer for indication
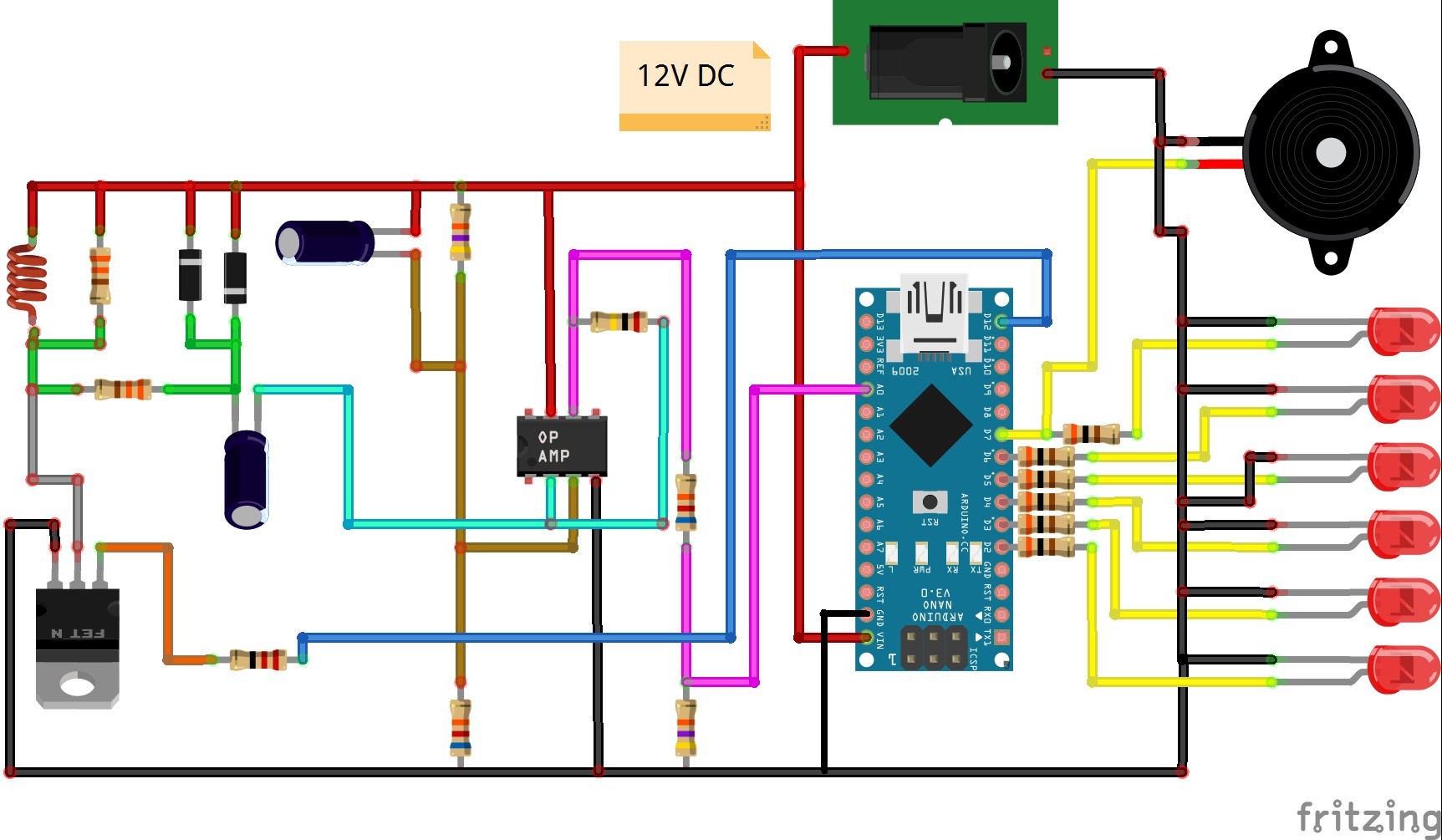
I presented a similar metal detector in one of my previous videos but it used a smartphone as an indicator and needed to be calibrated very often. Unlike it, this is a standalone device that self-calibrates by resetting the Arduino. Two lithium ion batteries connected in series are used to power the device. This time the detector is much easier to operate because it contains light and sound indication. Approaching the object increases the frequency and intensity of the LED. The search coil has a diameter of 20 cm and contains 25 turns of insulated copper wire with a cross section of 0.3 -0.5 mm square
 mircemk
mircemk





Thank you very much for your interest in this project. In fact, the code is taken from a Russian forum, not my own. The hardware is a variation of the "Pirate" metal detector. Thanks for the suggestions, in the coming period I will try to modify it with your suggestions and I will inform you what the results are