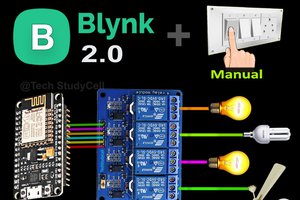
In this IoT project, I have shown how to make IoT-based Smart Home Automation using NodeMCU Cadio to control 4 home appliances from the Google Home, Amazon Alexa App, and Cadio.
 If the internet is not available, then you can control the home appliances from manual switches. During the article, I have shown all the steps to make this smart home system.
If the internet is not available, then you can control the home appliances from manual switches. During the article, I have shown all the steps to make this smart home system.

Tutorial Video on IoT Project using ESP8266 NodeMCU
This ESP8266 NodeMCU home automation system has the following features:
- Control appliances with the voice command using Google Assistant.
- Control appliances with the voice command using Alexa.
- Control appliances with the Cadio app.
- Control home appliances manually without internet.
- Monitor real-time feedback in the Cadio, Google Home, and Amazon Alexa App.
- Set Timer to control the devices automatically.
- Remember the previous state after the power cut (EEPROM).
- Can change the WiFi details through OTA.
- Don't have to write a single-line code. (No coding).
Required Components (Without PCB):

- ESP8266 NodeMCU.
- 4-channel 5V SPDT Relay Module.
- Switches or pushbuttons (4no)
Required Components (With PCB):
- Relays 5v (SPDT) (4 no)
- BC547 Transistors (4 no)
- PC817 Optocuplors (4 no)
- 510-ohm 0.25-watt Resistor (4 no) (R1 - R4)
- 1k 0.25-watt Resistors (5 no) (R5 - R9)
- LED 5-mm (5 no)
- 1N4007 Diodes (5 no) (D1 - D5)
- Push Buttons (4 no) or Switches
- Terminal Connectors
- 5V DC supply
Circuit Diagram of the ESP8266 IoT Project

This is the complete circuit diagram for this home automation project. I have explained the circuit in the tutorial video.
The circuit is very simple, I have used the GPIO pins D1 (GPIO-5), D2 (GPIO-4), D5 (GPIO-14), and D6 (GPIO-12) to control the 4 relays.
And the GPIO pins SD3 (GPIO-10), D3 (GPIO-0), D7 (GPIO-13), and RX (GPIO-3) are connected with pushbuttons to control the 4 relays manually.
I have used the INPUT_PULLUP function in Arduino IDE instead of using the pull-up resistors.
I have used a 5V mobile charger to supply the smart relay module.
Install CADIO Firmware on ESP8266
To make this project, first, you must install the Cadio Firmware on ESP8266.
- The CADIO dynamic firmware for ESP8266 NodeMCU is available to download from the Downloads Center.
- ESP8266 CADIO firmware consists of a single binary file located at the address 0x0.
- SPI flash mode is DIO.
- SPI flash speed is 40MHz.
- Make sure that the DoNotChgBin checkbox is activated.
- You should erase the current flash before start flashing the firmware to avoid any issues.
- Now click on Start to install the Cadio Firmware.
Now reset the ESP8266 NodeMCU and wait for 30 seconds. The inbuilt LEDs will start blinking which indicates it is in config mode.
Configure the NodeMCU Using Cadio App

- Turn off mobile data and connect the "CADIO" hotspot created by the ESP8266.
- Open the Cadio app, and click on the 3-dash icon.
- Select Configuration.
- Select Switches Mode: "PRESS" for the push button. For latched switch select "NORMAL"
- Select Relay Mode: "ACTIVE LOW". For active HIGH relay select "ACTIVE HIGH".
Enter GPIO for Relays and WiFi Details

- Select the Switch wiring "PULLUP".
- Now enter the GPIO pins for the Config button, Indicator LEDs and Devices as shown in the picture. Then click on the tick icon (in the top right corner).
- Click on YES to export the info file.
- Select the WiFi Name and enter the WiFi Password. Also, enter a unique unit name and tap on the tick icon.
- Wait for some time the dashboard will appear automatically.
Now we have to connect the ESP8266 NodeMCU to the circuit. Although you can make the circuit without using any PCB, to make the circuit compact I have designed a PCB.
Design the PCB for This ESP8266 Project

To make the circuit compact and give it a professional look, I designed the PCB...
Read more » Subhajit
Subhajit