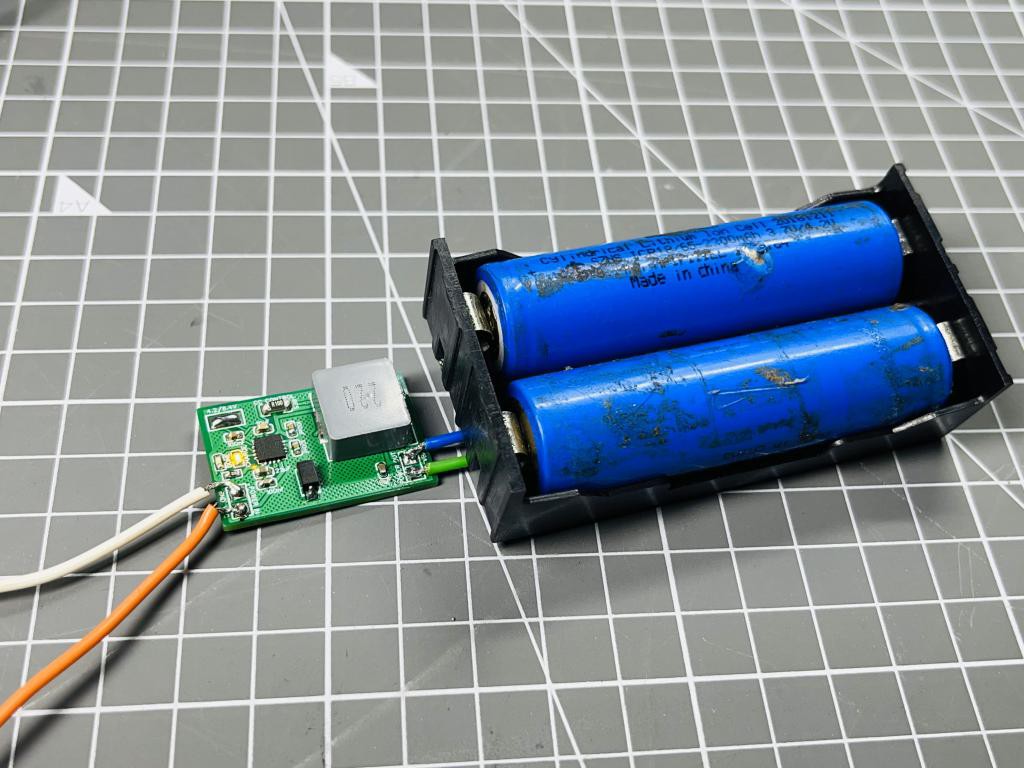
I am in the search of making a battery powered lab bench power supply, so that with a small form factor it becomes easy to carry while travelling on a project trip. This allows me to check and confirm the electronics components. But I need at least 2 lithium ion batteries in series so that I can efficiently use the buck and boost circuits in order to get a fixed high or low voltage. So, I faced many problems in design, the first one is to charge the batteries with a 12v adapter. Since it's 8.4v in series with 4.2v each li–ion battery. For this I need a charge circuit which can charge 8.4volts and 4.2 separately. Usually a battery changing circuit measures battery health, state of charge and then charge with constant current or constant voltage modes. Balance charging is also a crucial factor and plays an important role here if more than one battery is in series, but I don’t want to utilize that function here, because I am using identical cells from the same batch and manufacturer. So the internal chemical composition and charge properties are also identical in this case.
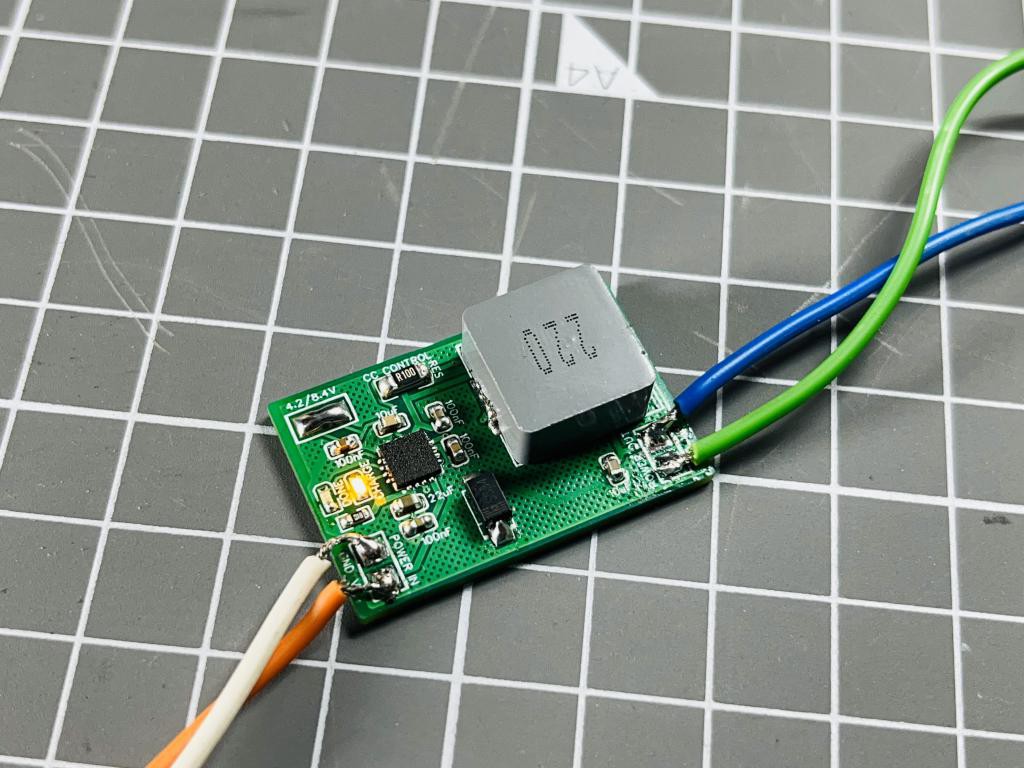
If you don’t have a balance charger and cells are identical, then the best practice of charging is to first charge the both cells separately to a constant voltage and then connect both of them in series and charge. In this way the initial voltage difference of the cells remains the same. And by chance I found an integrated circuit (TP5100) for that which can charge single and double cells (two in series). All the other battery protection, overcharge and modes are discussed below.
TP5100 Battery charger:
TP5100 is a step-down switching double 8.4V / 4.2V single lithium battery charge management chip and ideal for portable devices. Meanwhile, TP5100 built-in input overcurrent, undervoltage protection, over temperature protection, short circuit protection, battery temperature monitoring, reverse battery protection. TP5100 has a wide input voltage 5V-18V(which covers the 12v adaptor range). The battery trickle charging into pre-charge, constant current, constant-voltage three phase, pre-charge current trickle charge current is adjusted through an external resistor, the maximum charging current of 2A. TP5100 using frequency of 400kHz switching mode makes it highly efficient, and still maintains a smaller amount of heat in the large current charging.
Features:
Dual / single 8.4V / 4.2V rechargeable lithium battery
Built-in power MOSFET, a switching mode of operation
Programmable charge current, 0.1A - 2A
Programmable pre-charge current, 10% - 100>#/span###
Wide operating voltage, maximum reach 18V
LEDs for monitoring state of charge
Trickle charging mode
Modes of charging:
Let’s dive deep into the charging process and see what is happening during the changing process of a Li-ion circuit.
Trickle Charging:
Trickle charging (also known as pre-charging) occurs in two stages: It is a type of battery protection feature which is only enabled if somehow the battery gets over discharge.
Say if nominal voltage is 3.7v, and battery is over discharged (such as below 2.8V), recovery charging is performed first to prevent the battery from being damaged by excessive current. At this time, the software is not yet started, and it is a hardware-controlled behaviour. The "trickle charging" in this stage refers to the charging process after the battery is over-discharged and before it returns to the boot voltage. The current in trickle charging is 1/10 of the max charging current, which is 0.1C (If max charge current is 1A as an example, the trickle charging current is 100mA).
The commonly mentioned trickle charging refers to the charging process that continues for a period of time. It is a type of constant voltage charging and limits the value of charging current; once the battery reaches its normal voltage (3.7v), the trickle changing mode is shut down and Constant current charging mode is enabled.
Constant Current and Constant voltage charging:
During the standard...
Read more » Sagar 001
Sagar 001

 Bud Bennett
Bud Bennett
 tomcircuit
tomcircuit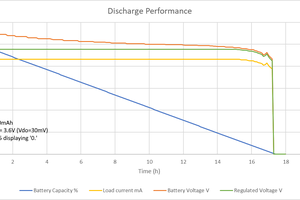
 George
George